VMware vSphere vs. vCenter vs. ESXi – Differences, Benefits, and More
Infrastructure Managed Services
It’s no secret that using virtualization can improve IT resiliency, optimize utilization rates, and increase efficiency. However, the data center virtualization process has many variables that should be considered before forging a path forward.
Once upon a time, pursuing a virtualization solution was relatively easy due to a limited number of products and solutions on the market. Today, there has been an explosion of virtualization vendors, with countless products and features available. This adds complexity for decision-makers and data center managers hoping to make a fast and informed decision that best suits their business requirements.
Jump-to Section
How do vSphere, vCenter and ESXi Work Together?
VMware Licensing Model – The Impact on vSphere, vCenter and ESXi
In this article you will discover the differences and interconnectivity of VMware vSphere, vCenter, and ESXi – three leading virtualization tools from VMware. With Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware leading to licensing changes, it’s even more useful to learn the individual components of VMware devices.
TL;DR:
- vSphere is VMware’s virtualization platform
- vCenter and ESXi are components that work within that platform to help organizations achieve their mission-critical goals
For a more detailed explanation on the differences, capabilities, and countless benefits of VMware vSphere, ESXi, and vCenter, continue below.
What Is VMware vSphere?
Developed by VMware, vSphere is a cloud computing virtualization platform. It should not be thought of as a product, rather a product family containing supportive software and management tools. Another way of looking at it is that vSphere is a suite of virtualization solutions that includes vCenter, ESXi, vRealized Operations, and more.
What Does vSphere Do?
The core ability of vSphere is the centralized management of your virtual machines and virtual environment. The vSphere client offers a very wide range of functionality, although this will vary from organization to organization based on the components of the suite each uses. Some of the most important functionality offered by vSphere include the following:
- Easily creates and manages multiple virtual machines
- Migrates workloads and data center maintenance live and avoid downtime
- Manages offices remotely with few or no local IT admins
- Creates a flexible environment customized to your organization’s specific needs and requirements
Benefits of vSphere
vSphere offers a very wide range of benefits, but some of the most important include:
- Improved security and protection of valuable data
- Reduced IT hardware costs
- Business continuity solutions
- Reduced IT footprint
- Improved service levels
- Improved application quality
What Is vCenter Server?
vCenter is a component of VMware’s vSphere. It is designed to offer advanced server management capabilities through a centralized platform. It also offers improved visibility across hybrid cloud environments, while automating and delivering virtual infrastructure. Moreover, vCenter allows you to manage ESXi hosts, as well as virtual machines.
If you use VMotion, VMware High Availability, or VMware Update Manager, vCenter Server is the application for managing these features.
What Does vCenter Do?
Some of the key features and capabilities of vCenter Server include the following:
- Allows users to access instances with a single sign-in
- Searches your entire inventory, including VMs (virtual machines) and hosts, with a single click
- Runs up to 2,000 hosts and 35,000 virtual machines using a single instance
- Solves problems faster with customizable triggers
- Captures host configuration/profile information
Benefits of vCenter
vCenter offers many important benefits, including:
- Simple deployment and centralized control and visibility
- Easily manage servers/virtual servers
- Full scalability across hybrid cloud environments
- Proactive optimization
vCenter vs. vSphere
It’s difficult to compare vSphere vs. vCenter because vCenter is a component of vSphere – not a competing product. When looking at the difference between vSphere and vCenter, it’s better to think of vCenter as component of a vSphere deployment, that enabled advanced management scenarios.
What Is VMware ESXi?
VMware ESXi is yet another component of vSphere. It is also one of the most popular components because it delivers the core virtualization services organizations need. It is a bare-metal hypervisor, that sits atop the ESXi host, and delivers an array of critical capabilities and features.
Understanding Hypervisors
With ESXi being an example of a hypervisor, it’s important to define exactly what a hypervisor is.
A hypervisor is a specialized layer of software that allows multiple VMs to run on a single physical machine by abstracting and sharing the underlying hardware resources. Examples of hardware being shared could be CPU, memory, storage, and network.
So ESXi is a type of hypervisor, specifically a VMware hypervisor, installed directly onto a physical machine, which creates the separation necessary to divide it into one or more virtual machines. And thanks to ESXi’s small footprint, it requires minimal system resources for itself, leaving more for the VMs to use. It is also highly flexible, delivers outstanding security, and offers an intuitive interface that’s easy to use.
What Does ESXi Do?
ESXi is a critical component of vSphere and is responsible for:
- Allowing organizations to consolidate IT hardware for improved utilization
- Delivering improved performance and helping create a competitive advantage
- Streamlining the administration of IT
- Reducing hardware resources and improving efficiency
- Reducing capital and operating expenses (CapEx and OpEx)
Benefits of ESXi
Some of the benefits offered by an ESXi environment include the following:
- Delivers a user-friendly experience
- Offers enhanced security and protects important data
- Reduces the IT footprint
- Offers reliable, predictable performance
vCenter vs. ESXi
ESXi and vCenter are two different components of vSphere. vCenter is advanced server management software usually deployed as a pre-configured Linux virtual machine, while ESXi is a virtualized hypervisor that is installed only on physical machines. These are both part of the vSphere solution.
ESXi vs. vSphere
Like vCenter, ESXi is a component solution designed to operate within the vSphere suite. When assessing vSphere vs ESXi, ESXi is designed to create and manage multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, while vSphere is an entire solution designed to improve your IT resilience by leveraging virtualization with your physical IT assets.
Table Summarizing ESXi vs vSphere vs vCenter
vSphere, ESXi and vCenter all serve different purposes for the VMware product. The table below summarizes the main points and key distinctions between the three components.
| Characteristic | VMware ESXi | VMware vCenter | VMware vSphere |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Virtualization platform (bare-metal hypervisor) | Centralized infrastructure management tool | Integrated virtualization suite |
| Main task | Deploy and run virtual machines | Manage multiple ESXi servers | Combines core hypervisor and management tools with advanced capabilities |
| Features | Run and configure VMs on a standalone host | Centralized control, host pooling, and cluster management | Advanced tools like live migration, resource scheduling, and storage virtualization |
| Licensing | Available in both free and paid editions (through vSphere licensing) | Only available as a paid license through vSphere | Tiered licenses offering various feature sets (Essentials, Standard etc) |
| Limitations | Lacks integration with vCenter and advanced features in free edition | Commercial use only, scalability limits based on license | Functionality varies based on selected license tier |
| Suitability | Standalone ESXi is ideal for labs, testing, and lightweight deployments | Essential for any business running more than one ESXi Host | Suited for businesses needing robust, scalable virtualization solutions |
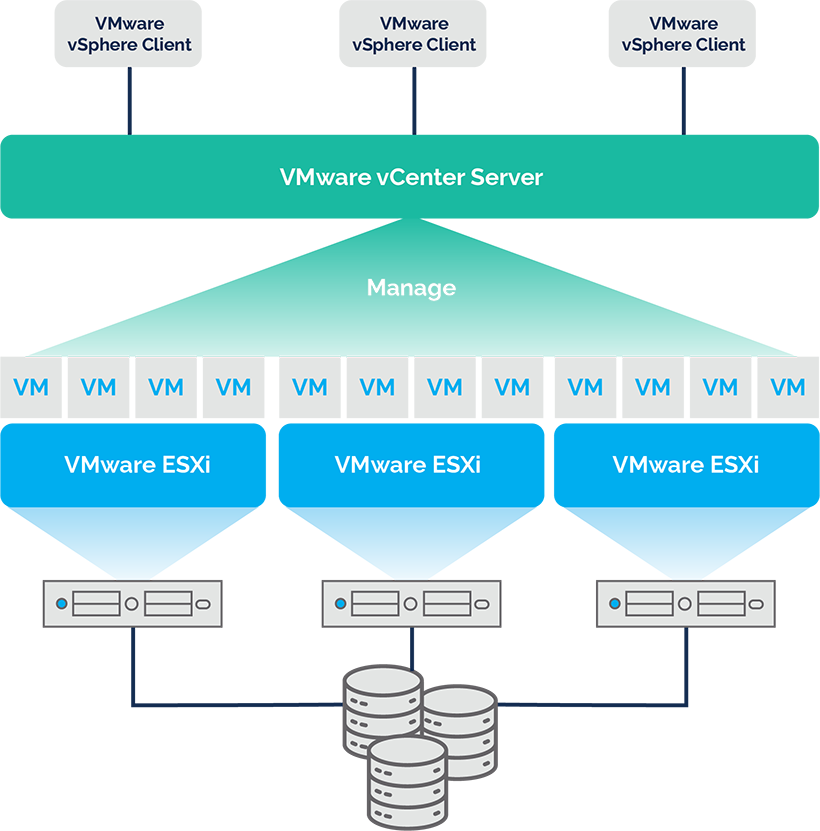
How do vSphere, vCenter and ESXi Work Together?
A close integration between ESXi, vCenter Server, and the larger vSphere platform is essential to VMware’s virtualization platform. Each component serves a specific function, however together their functionality provides a basis for virtual environments that are highly available.
ESXi, VMware’s hypervisor, is a core component. As established it virtualizes the underlying physical hardware on the VMware server. However, individual management is limited and less effective for ESXi hosts, especially when scalability is required.
This is where vCenter comes in. A single vCenter can be used as the central point of control for up to 2,500 ESXi hosts, giving administrators access to the entire virtual infrastructure through a single interface. Features like vMotion (live virtual machine migration), High Availability (HA), Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), and template-based virtual machine provisioning are made possible by vCenter’s organization of hosts into data centers.
vSphere, as the management platform, essentially binds everything together. ESXi, vCenter and APIs integrate and interact with eachother due to vSphere accessibility.. vSphere applies policy, automation, standards, and monitoring to the application.
In order to provision and manage virtual machines, distribute workloads, and recover from data center outages, vCenter operates by interacting with ESXi hosts. This communication is scalable and seamless thanks to vSphere. When combined, they turn individual servers into a single, resilient infrastructure that can handle anything from enterprise apps to development workloads.
VMware Licensing Model – The Impact on vSphere, vCenter and ESXi
An important contextual point to raise regarding the relationship between ESXi, vCenter and vSphere is regarding licensing, which was altered after Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware in 2023.
After purchasing VMware, Broadcom simplified the licensing models available to two offerings: VMware vSphere Foundation (VVF) and VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF). Both models include all three core elements (vCenter, vSphere and ESXi), however VVF is more suitable to traditional on-premises infrastructure for small to medium businesses, while the VCF approach is suitable for hybrid cloud ready enterprises.
This shows how the three components can be utilized differently, depending on the IT infrastructure.
Support Your VMware Virtual Environment with Park Place Technologies
Park Place’s Managed Services is a full suite of managed IT infrastructure solutions that brings order to managing an organization’s critical physical and virtual infrastructure while eliminating chaos and accelerating business transformation. ParkView Automated Support™ empowers you to efficiently Discover, Monitor, Support and Optimize your IT infrastructure, including cloud environments like VMware’s vSphere platform, vCenter Server, ESXi hypervisor, vSAN, Horizon, and Horizon DaaS.
We combine third-party VMware software support and data center hardware monitoring for physical infrastructure with our server management services for physical, virtual, and cloud technologies to proactively identify potential faults. The result? A one-stop shop for traditional, virtual, and hybrid data centers – much like manufacturer-provided services, but with distinct advantages in terms of cost, responsiveness, and flexibility!
Three tools, one managed service provider for your VMware virtual environment. Contact Park Place Technologies to get started today!
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is an ESXi host?
An ESXi host is a physical server that hosts VMware's ESXi hypervisor, by which you can install and control virtual machines (VMs). It masks the hardware layer and provides a platform to run multiple configuration-independent VMs on one physical server. ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor since it installs on the server directly without needing a base operating system.
-
What is the difference between ESX vs ESXi?
Both ESX and ESXi are VMware hypervisors. The main difference is that ESX had a Linux Service Console embedded within it, whereas ESXi is a more stripped-down version without the console, which improves security and performance. VMware ended support for ESX in favor of ESXi with vSphere 5.0, so from then onwards ESXi is the default hypervisor.
-
What is the difference between ESXi vs VMware?
ESXi is a product developed by VMware. So, VMware is the company, and ESXi is one of its hypervisors. Comparing the two is like comparing a brand to one of its tools—ESXi is part of VMware’s broader virtualization suite.
-
What is the difference between VMvisor vs ESXi?
VMvisor is another name for VMware ESXi, often used in documentation or product labels. There is no functional difference—VMvisor refers to the same lightweight, bare-metal hypervisor as ESXi.
-
What is the difference between VMware vs vSphere?
The difference between vSphere and VMware is that VMware is an organization which owns a series of virtualization and cloud offerings, whereas vSphere is a collection of VMware products being used for the management of virtualized data centers.